Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Description
You are given an m x n grid where each cell can have one of three values:
0representing an empty cell,1representing a fresh orange, or2representing a rotten orange.
Every minute, any fresh orange that is 4-directionally adjacent to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
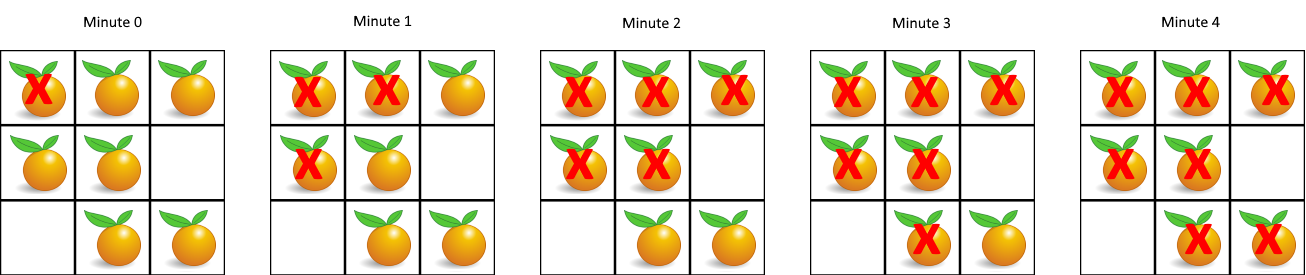
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[0,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10grid[i][j]is0,1, or2.
Idea
We could use breadth-first-search (BFS) to explore the graph starting from the rotten oranges.
- We add the rotten orange locations to a queue and maintain the count of fresh oranges.
- If fresh count becomes zero or the queue is empty, we can stop exploring.
- Every iteration, we start from the rotten oranges and explore the four directions. We change the fresh orange neighbors to rotten and add the locations to the queue.
- If the fresh count can reach to zero, we return the number of steps during the BFS. Otherwise, return -1.
Complexity: Time , Space .
Python
class Solution:
"""6 ms, 17.32 mb"""
def orangesRotting(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
(m, n), fresh, q, res = map(len, (grid, grid[0])), 0, deque(), 0
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if grid[r][c] == 2:
q.append((r, c))
elif grid[r][c] == 1:
fresh += 1
while q and fresh > 0:
res += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
x, y = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in [(1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if nx < 0 or nx == m or ny < 0 or ny == n: continue
if grid[nx][ny] == 0 or grid[nx][ny] == 2: continue
fresh -= 1
grid[nx][ny] = 2 # serve as visited
q.append((nx, ny))
return res if fresh == 0 else -1
Rust
A couple caveats.
- If using
usizefor row and column indices, we can useusize::MAXto replace-1in the four directions. - No need to check boundary less than 0 since
usizewas used.
use std::collections::VecDeque;
/// leet 994, 0 ms, 2.25 mb
impl Solution {
pub fn oranges_rotting(mut grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let (m, n, mut res, mut fresh, mut q) = (grid.len(), grid[0].len(), 0, 0, VecDeque::new());
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
match grid[i][j] {
2 => q.push_back((i, j)),
1 => fresh += 1,
_ => {}
}
}
}
while !q.is_empty() && fresh > 0 {
for _ in 0..q.len() {
let (x, y) = q.pop_front().expect("not empty");
for (dx, dy) in vec![(0, usize::MAX), (usize::MAX, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0)] {
let (nx, ny) = (x + dx, y + dy);
if nx > m - 1 || ny > n - 1 || grid[nx][ny] == 2 || grid[nx][ny] == 0 { continue; }
fresh -= 1;
grid[nx][ny] = 2;
q.push_back((nx, ny));
}
}
res += 1;
}
if fresh == 0 { res } else { -1 }
}
}